The article defines CMS as a software application that helps create, manage, and modify digital content. CMS examples include WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla,… Learn more about CMS definition and its role in website development and management.
In this article:
What does CMS stand for?
CMS meaning – Why should you care?
What is Open source CMS?
What is Proprietary CMS?
What is Headless CMS?
Best CMS – Pick the right!
What does CMS stand for?
A CMS, or Content Management System, is defined as a software tool that allows users to manage content on their websites using simple drag and drop without knowing how to code at all.
Your CMS’s “content” might include:
- Blogs
- Videos
- e-commerce items
- Forums
- Memberships
Definitely, there could be a variety of content at once! You may handle as many various sorts of content as you need with the support of a CMS platform.
CMS meaning – Why should you care?
- CMS enables non-developers and everyone:
Usually, to make a change, even a simple content update, you have to download code files from the server, fix the HTML code by hand, then upload it back to the server. This is such a tricky process. With CMS software, you will be able to create, manage, edit, and launch content through a friendly interface everyone can use.
- CMS makes teamwork easier and safer:
Many users can access and work on the back end of a CMS at the same time, which helps improve workflows and productivity throughout your company. With CMS user management, you can control what your members do and don’t. For instance, content creators can have all the rights necessary to modify content, but they won’t be able to uninstall plugins or otherwise radically alter the function of the website.
- CMS saves your time with sexy design templates:
With a variety of cms templates, you can rapidly alter the appearance of your site so that it appears well on every device and improves your UX. Remember, 61% of online users will drop your site if they have a poor experience with it.
- CMS provides SEO features and extensions:
– Create your page titles and meta descriptions
– Customize friendly URL structures
– Create XML sitemaps
– Add alt text
– Include navigation
– Optimize page load times
What is Open source CMS?
An open source CMS makes the codebase of software available to everyone. As a result, your business with access to the source code can change the software and add any features they require. You can check out open source CMS software for free, with no licensing, upgrade fees or contracts. However, some services may incur expenses, such as:
- Technical assistance with installation and setup
- Software customization outside of the basic offering
- Templates, add-ons, and plug-ins
- Management and staff training
- User support, such as regular CMS software updates
Although open source CMS helps your business optimize the cost and the modules continually improve by community, they sometimes face attacks as anyone can see the code.
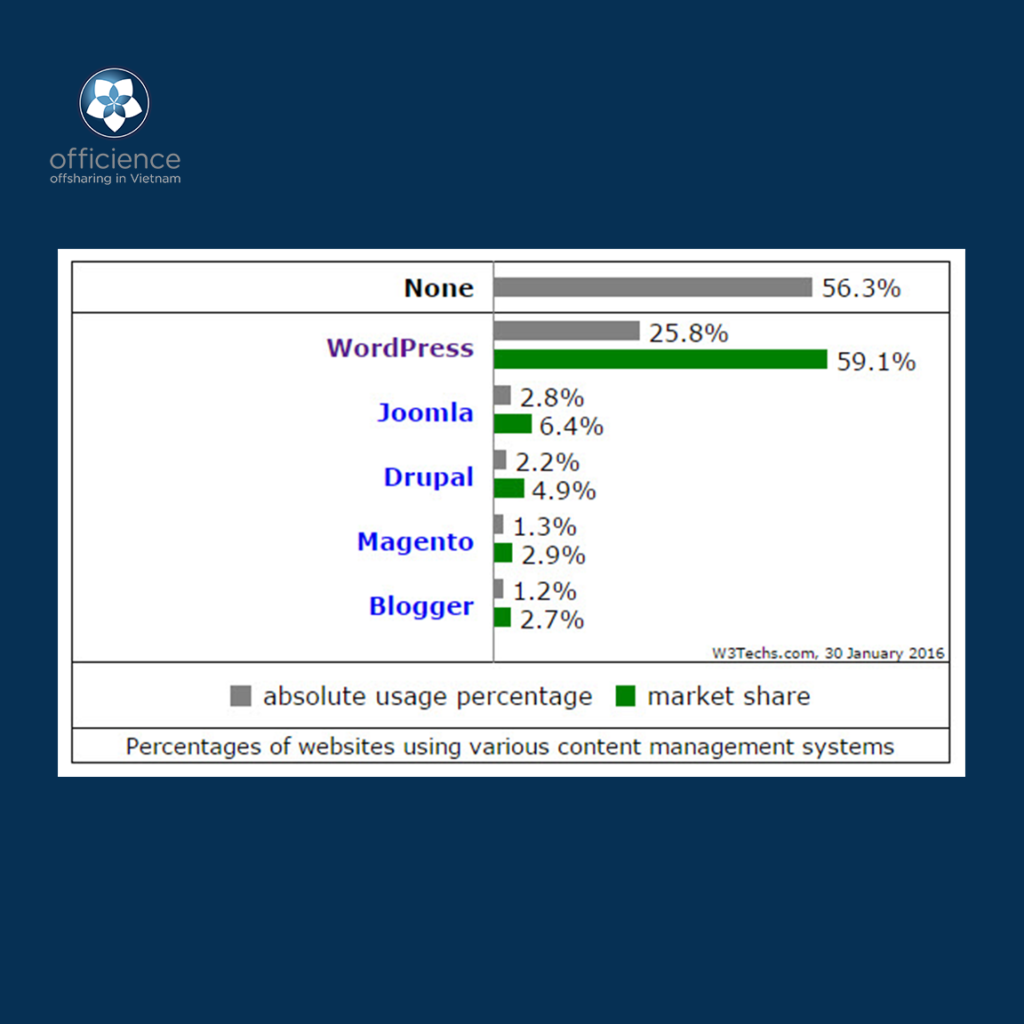
Examples of open source CMS platforms:

What is Proprietary CMS?
Commercial CMS is another term for proprietary CMS. Opposite to open source CMS, proprietary CMS is created and controlled under a single business and closed to the public. If you currently have a website or back-end system, it may be more difficult and costly.
If you choose a proprietary CMS controlled by the other company, you will know exactly who to take responsibility for if there is a problem. The main downside of a proprietary CMS is that your reliance on others makes switching more difficult and expensive.
Examples of proprietary CMS platforms:
What is Headless CMS?
Traditional CMS gave non-tech users a chance to set up their content in the era of website browser building. However, because they were not made to keep up with trendy technology, we now require a Headless CMS as a result of new devices and displays being born (mobile apps, IoT,…) besides the website.
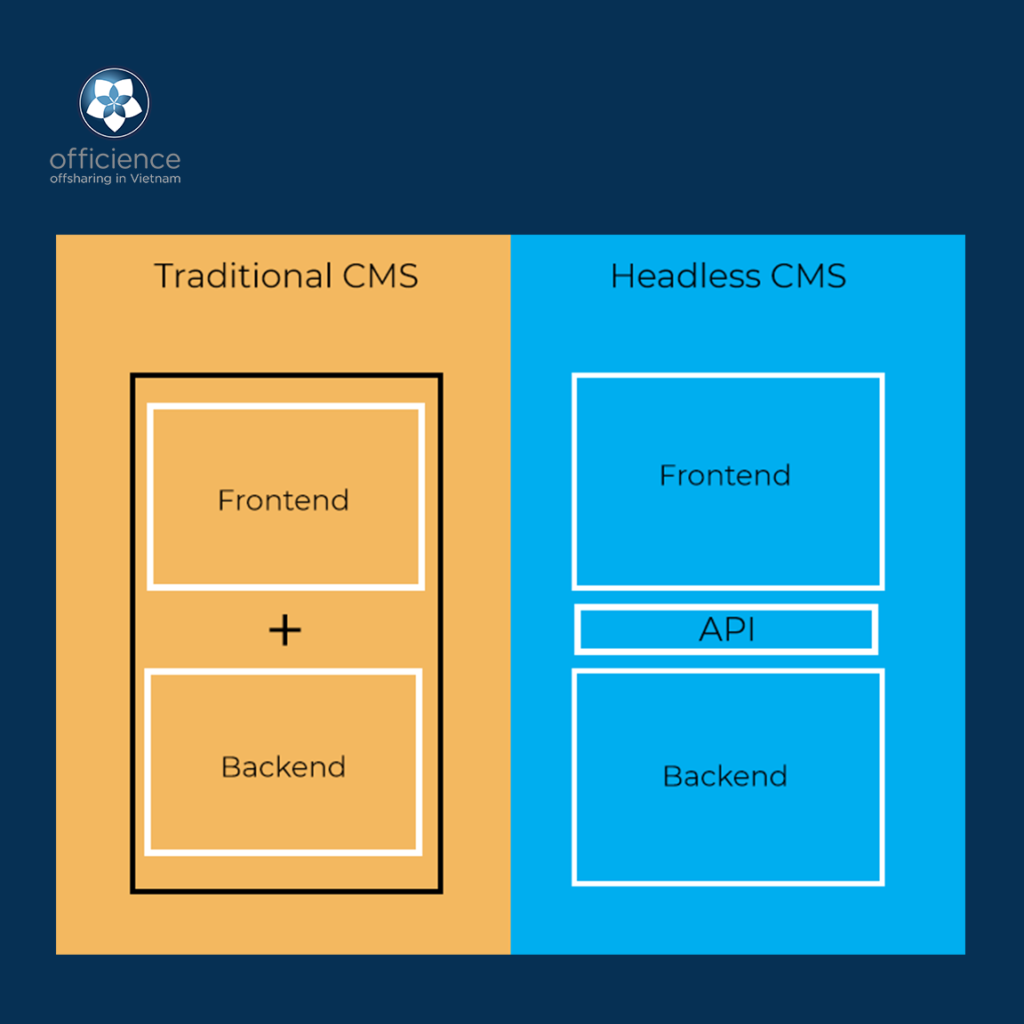
But how does Headless CMS work? While traditional CMS sets up your content in one place for both “backend” and “front-end”, a headless CMS manages the content at the backend and publishes it on the front-end through an API. In this way, you can display content on any device because they are independent.

Headless CMS unifies content into a single content hub, eliminates manual processes like copy and pasting and makes content reusability a breeze on different cases, campaigns or devices. In other words, Headless CMS can easily apply the COPE principle: Create Once, Publish Everywhere.
Examples of headless CMS platforms:
Best CMS – Pick the right!
Any new CMS is a big effort that will influence numerous aspects of your organization. Make sure you receive input and buy-in from a diverse panel and be prepared to hear divergent viewpoints. While IT will want to take a technical approach to lower risks, marketing will be keen to get started on content creation.
If your organization lacks strong in-house developers, you should consider hiring an implementation partner or agency. They will assist you in selecting a CMS and ensuring that it fits into a bigger digital strategy. After the first installation, many partners continue to provide assistance.


